Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
The "Teaching Welding Robot" has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. These robots offer precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. As Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in robotics, states, "Teaching Welding Robots are not just machines; they are tools to elevate craftsmanship."
In practice, these robots learn from human instructors. They mimic the welding techniques demonstrated, ensuring accuracy in every weld. Operators can program these robots through an intuitive interface, making the teaching process straightforward. However, challenges remain. For instance, robots may struggle with complex tasks that require human-like intuition.
Embracing a Teaching Welding Robot requires adaptation. While they enhance productivity, they also demand that operators refine their skills. Balancing automation with the human touch can lead to better outcomes. Looking ahead, the industry must address these nuances, ensuring both robots and humans work together harmoniously.

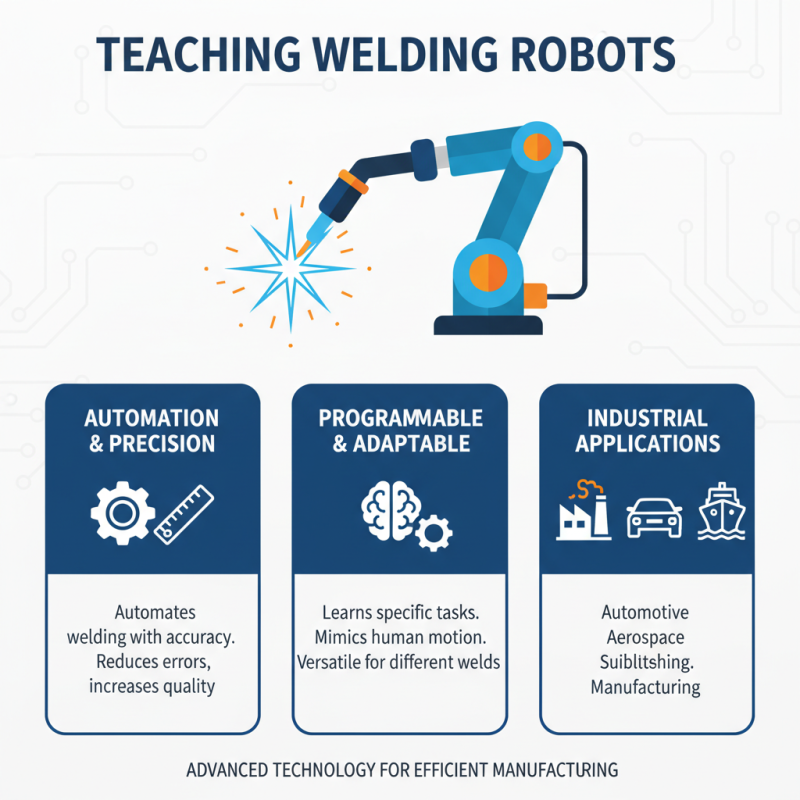
A teaching welding robot is an advanced technology used in manufacturing. It helps automate the welding process with precision and efficiency. These robots are programmed to perform specific tasks related to welding operations. They can mimic human movements, making them valuable in various industries.
The teaching process involves using a handheld device to guide the robot. Operators can demonstrate the desired welding paths and techniques. The robot then records this information. This approach allows for quick adjustments and easier training. However, relying solely on these robots can present challenges. They may struggle with unexpected obstacles or changes in the production environment.
Adopting teaching welding robots requires thoughtful consideration. Not every operation can be fully automated. Workers must still monitor and oversee the process. This blend of automation with human oversight creates a harmonious workflow. Nonetheless, the potential drawbacks necessitate ongoing evaluation of the technology's effectiveness. Balancing automation and human skill is key to maximizing efficiency.
Teaching welding robots have become essential in modern manufacturing. They streamline production processes and improve safety. The main components of these robots include hardware and software, which work together seamlessly.
The hardware typically consists of robotic arms, welding tools, and sensors. Robotic arms are designed for flexibility and precision. They can maneuver through various positions depending on the welding task. Sensors ensure that the robot can detect materials and maintain the correct height and angle during welding. On the software side, programming languages like Python and specialized software platforms are used to teach the robots specific tasks. These programs analyze welding patterns and optimize the process. According to a recent industry report, automating welding can enhance production efficiency by up to 30%.
Tip: When choosing a teaching welding robot, look for systems with user-friendly interfaces. Complicated software can hinder productivity and increase training time.
Additionally, it's crucial to assess the robot's adaptability. Some models might struggle with irregular shapes or surfaces. Understanding the limitations can prevent project delays. Regular updates to the software can improve overall functionality, but they should be approached cautiously. A well-balanced approach helps ensure consistent performance and reliability.
Tip: Regular maintenance directly impacts the longevity of welding robots. Schedule routine checks to avoid unexpected breakdowns and keep operations running smoothly.
The teaching process for welding robots involves a series of steps that allow these machines to learn and adapt. Initially, operators physically guide the robot through the desired welding path. This demonstration serves as the foundation for the robot's memory. The robot uses sensors to track its movements, capturing data on speed and angle. This data helps it replicate the welding task accurately.
However, the process isn't always straightforward. Environmental variables can lead to inconsistencies. For example, even a slight change in temperature can affect welding quality. Robots must adjust to these conditions to produce optimal results. Operators often need to refine the robot's programming through trial and error, identifying areas for improvement.
As robots learn, they can develop a level of autonomy. Yet, this doesn't mean they can function independently without oversight. Regular monitoring is crucial to ensure they adapt correctly. Unexpected challenges may arise, requiring human intervention. Continuous feedback loops between the robot and its operators improve efficiency.
Ultimately, embracing imperfections allows for better learning and skill enhancement in welding tasks.
Teaching welding robots are increasingly common in various industries today. They enhance precision in welding tasks. Their ability to learn from human operators makes them adaptable. In automotive manufacturing, for example, they streamline processes. These robots reduce errors and improve weld quality, making production faster. Anomalies in welds can still occur, requiring human oversight.
In construction, teaching welding robots perform complex tasks. They often work on high structures, where human access is limited. This minimizes risk for workers while ensuring efficiency. However, the challenge remains in programming these robots. It demands skilled technicians who can translate human techniques into robot language. Misinterpretations can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs.
The use of teaching welding robots is also seen in aerospace. They weld intricate parts with great accuracy. Yet, flaws may still arise, demanding ongoing evaluation. The integration of these robots is not seamless. Companies face hurdles in training staff and maintaining the machinery. Adaptability and human instruction are crucial for optimal performance.
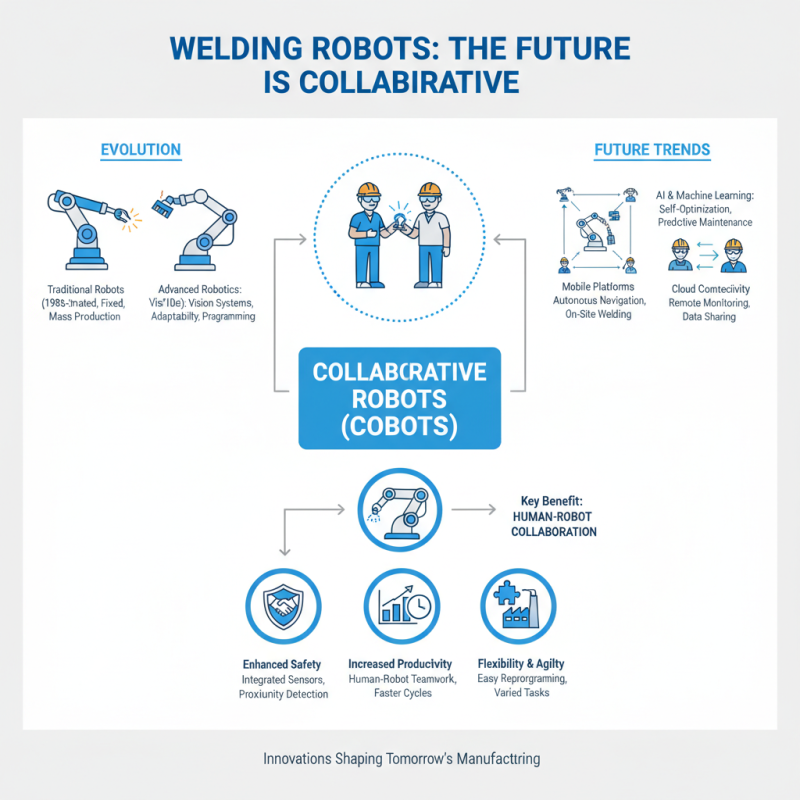
Welding robots are evolving quickly. Innovations are shaping their future. One significant trend is collaborative robots. These machines work alongside humans. They enhance productivity while ensuring safety. Collaboration in the workspace is becoming essential. It allows for flexibility in various industries.
Another promising trend is artificial intelligence. AI is being integrated into welding robots. This technology helps them learn and adapt. As they perform tasks, they collect data. This data informs future operations, improving efficiency. The robots can make adjustments in real-time. This leads to higher quality welds and fewer mistakes.
However, challenges remain. Programming these robots can be complex. Not every workplace is ready for this change. Training is often necessary to gain skills. Some workers worry about job security. It’s vital to address these concerns as technology advances. Balancing innovation and human elements is crucial in this field.






