Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
The landscape of Traditional Welding Equipment is changing. As industries evolve, so too do the tools and technologies we use. John Smith, a respected expert in the field, states, "Innovation is the key to bridging traditional practices with modern needs." His insight captures the essence of current trends.
Welders face new challenges and demands. From automation to advanced materials, the landscape is vast. Traditional Welding Equipment is not just about the tools themselves; it's about adapting to a new reality. Efficiency and safety are more critical than ever.
As we look toward 2026, we must recognize that innovation must remain at the forefront. Technologies that once seemed reliable may require reevaluation. Embracing change can be daunting but necessary. The future of Traditional Welding Equipment will demand flexibility and a willingness to rethink established norms.

As we approach 2026, traditional welding equipment is set to undergo significant transformations driven by emerging technologies. A notable trend is the integration of automation in welding processes. Automated systems can enhance precision, reduce human error, and increase production rates. However, reliance on these systems raises concerns about job displacement. Workers may need to adapt to new roles, focusing on oversight rather than hands-on tasks.
In addition, advancements in materials used in welding equipment are changing the landscape. New composite materials are lighter and more durable, providing better performance and longevity. While these innovations promise efficiency, there’s a learning curve. Welders will need training to work with these advanced materials and adapt to their unique characteristics.
Moreover, real-time data monitoring is becoming increasingly common. Sensors embedded in welding equipment can provide feedback on process quality and safety. This feature allows for immediate adjustments, ensuring optimal results. Yet, it can also overwhelm operators with information, leading to decision fatigue. Balancing technology and human intuition will be essential in this evolving field.
Welding safety standards are evolving rapidly. New technologies improve protection for welders. Advancements in personal protective equipment (PPE) play a crucial role. These items are becoming more comfortable while providing better resistance to heat and sparks. Lightweight helmets and gloves help improve mobility, allowing for more fluid movement during welding tasks.
Integration of smart technologies in safety gear is on the rise. Helmets equipped with sensors help monitor work environments, detecting harmful gases and excessive temperatures. This data empowers welders to make better decisions on-site. However, the challenge remains in ensuring all workers are trained to use these new tools effectively.
Regular updates to safety protocols are essential. Companies need to prioritize training and education on these advancements. Many welders still rely solely on outdated practices. This creates gaps in safety and increases risks. Continuous improvement and adaptation are needed for a safer work environment.

In 2026, the trend towards sustainable materials will significantly influence welding equipment development. Manufacturers are focusing on eco-friendly alternatives that reduce environmental impact. Recyclable materials are becoming increasingly popular. These materials can enhance the performance of welding machinery while also preserving resources.
Using sustainable materials does come with challenges. Some materials may not have the same strength or durability as their traditional counterparts. This requires engineers to innovate and adapt designs. The resulting products may fall short of expectations at times. However, the push for sustainability drives continuous improvement in welding technologies. The industry must evolve to find better solutions.
Welding professionals are also adapting their techniques to work with these new materials. Training programs are emerging to address the skills gap. These programs focus on techniques for effective welding with sustainable options. Proper training is critical for success, as improper methods can lead to weak joints. The ongoing transition highlights the need for reflection and adjustment in practices throughout the welding sector.
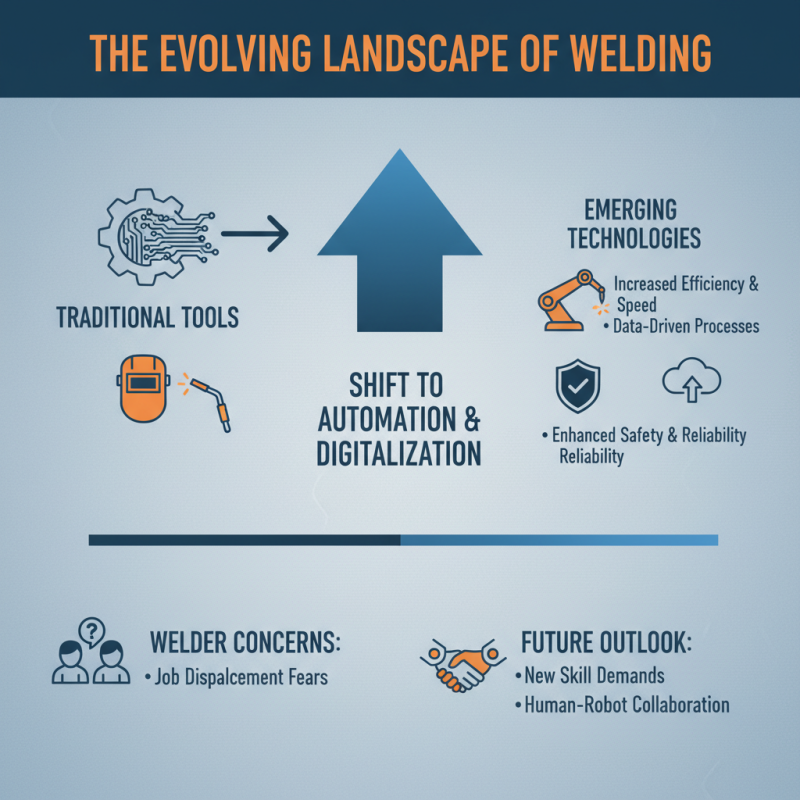
The landscape of traditional welding tools is shifting rapidly. We are entering an era where automation and digitalization influence how welding equipment is manufactured and used. Emerging technologies aim to enhance efficiency and safety, making welding processes faster and more reliable. However, not everyone embraces these changes. Some skilled welders worry about job displacement.
Consumer preferences are changing too. There is a growing demand for portable and user-friendly welding tools. Lightweight designs are appealing, especially for those working in tight spaces. Yet, the rise of these new tools can sometimes overlook the old methods’ reliability. Traditional techniques still hold value but face pressures. Many are concerned about the knowledge gap that may arise when younger generations focus more on new technology.
Market dynamics also play a significant role. A fluctuating economy can influence production costs and material prices. With sustainability becoming central, manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly options. But, adopting green practices can be costly. It requires a fine balance between innovation, tradition, and affordability. The welding industry stands at a crossroads. Addressing these challenges will demand critical reflection and adaptation from all stakeholders involved.
Automation and robotics are transforming traditional welding techniques. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the welding automation market is expected to reach $8.1 billion by 2026. This rapid growth reflects the industry's push towards efficiency and precision. Automated welding systems can often complete tasks faster than manual methods, reducing production time significantly.
However, the transition to automation is not without challenges. Many skilled welders fear job displacement. The balance is delicate. Companies must retrain their workforce to thrive in an automated environment. For instance, implementing collaborative robots, or cobots, can augment human efforts rather than replace them. This allows for a more harmonious integration of technology and craftsmanship.
Data from the International Institute of Welding highlights that approximately 30% of welding operations still rely heavily on manual labor. The persistence of traditional methods indicates a need for continuous training and adaptation. Welders who embrace new technologies can harness the advantages of automation while maintaining their artistry. Ultimately, the shift towards automation must consider both efficiency and human skill.
The chart above illustrates the top trends in traditional welding equipment for 2026. Automation and robotics are expected to have the highest impact on the welding industry, while advancements in safety, energy efficiency, and materials continue to evolve as important factors.